If you forget or lose the root password to your MySQL, you can still gain access and reset the password if you have access to the server and a user account with sudo privileges.
Reset – Change the MySQL root Password on Ubuntu 20.04
Reset – Change the MySQL root Password on Ubuntu 22.04
STEP 1: Check your MySQL version running on Ubuntu. For different MySQL versions, there may be different commands to reset the MySQL root password. To check MySQL version use the following command in terminal.
mysql --version
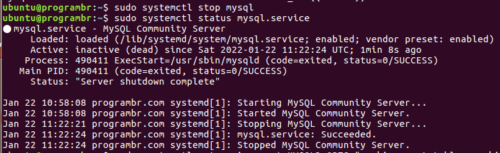
STEP 2: To change the MySQL root password, you’ll need to shut down the MySQL server. To stop MySQL server, run the following command in terminal.
sudo systemctl stop mysqlSTEP 3: Now check the MySQL server status. Does the MySQL server shutdown or not? To check MySQL server status run the following command in terminal.
sudo systemctl status mysql
Restarting MySQL Server With the --skip-grant-tables option
MySQL server allows accessing the database command line with root privileges without providing a valid password. To do this, you need to stop the database from loading the grant tables, which store user privilege information.
STEP 5: Now restart the MySQL server without granting the tables and networking check. To skip grant tables and network check, use the following command in terminal.
sudo systemctl set-environment MYSQLD_OPTS="--skip-grant-tables --skip-networking"
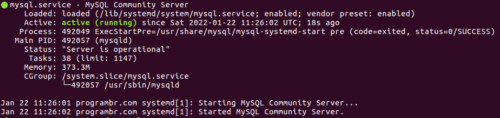
STEP 6: Now, start the MySQL server. To start the MySQL server, use the following command in terminal.
sudo systemctl start mysqlSTEP 7: Check the MySQL server status. Does the MySQL server start or not? To check MySQL server status run the following command in terminal.
sudo systemctl status mysql
Change MySQL Root Password
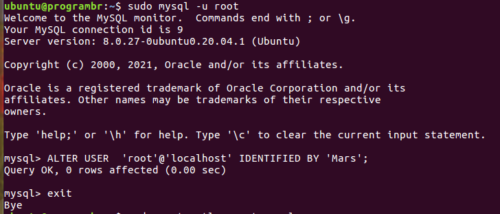
STEP 8: You need to log in as a root user to MySQL. Now, you can now log in as a MySQL root user without a password. After logging in, you will see the mysql> prompt.
sudo mysql -u root
STEP 9: Now, it’s time to change the MySQL root password or set the new password. To set the new password for MySQL root user use the ALTER command.
Example:- ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'New_Password';Don’t forget to change the New_Password to your desired new password as per MySQL level and security rules. Here I am setting the new password as Mars.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Mars';
STEP 11: The password is now changed. After changing the MySQL root password, log out from MySQL. Type exit and hit Enter to log out from MySQL.
exit
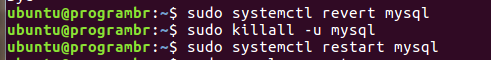
STEP 12: Now kill all the processes of MySQL, and restart the MySQL server. To kill all the processes of MySQL, use the following command
sudo killall -u mysql
STEP 13: To restart the MySQL server, Use the following command
sudo systemctl restart mysql
STEP 14: Now, You are ready to log in as a root user with the recently set new password.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Conclusion
Congratulation, MySQL’s root password is successfully changed. You can log in MySQL server with the new password.
See Also
| Company Name | Open Date | Close Date | Record Date | BB Price Per Share (₹) | Issue Size Shares (Cr) | Issue Size Amount (₹-Cr) |
| eClerx Services | 3 Feb | |||||
| Technocraft Industries | 1 Feb | |||||
| Kama Holdings | 31 Jan | 13 Feb | 23 Dec 2022 | 14500 | 50.03 | |
| Tips Industries | 27 Jan | |||||
| Cosmo First | 27 Jan | |||||
| Triveni Turbine | 17 Jan |