The shred command overwrites the contents of files in a way that makes it very difficult to recover them.
When you delete a file or delete it from the trash, from Linux or any other operating system, it is not completely erased from the hard drive.
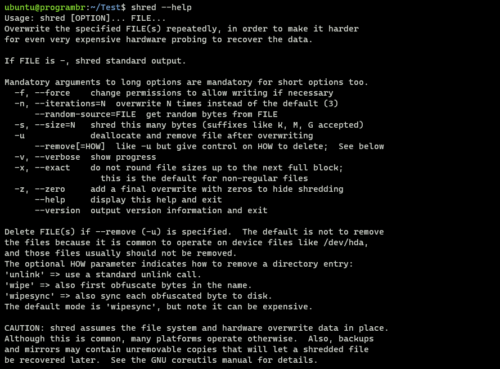
shred --help
shred --version
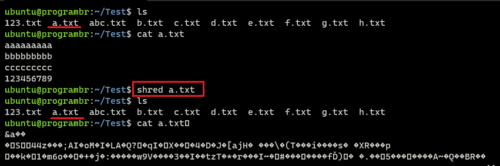
shred a.txt
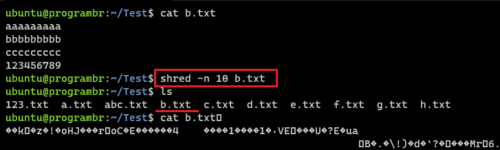
shred -n 10 b.txt
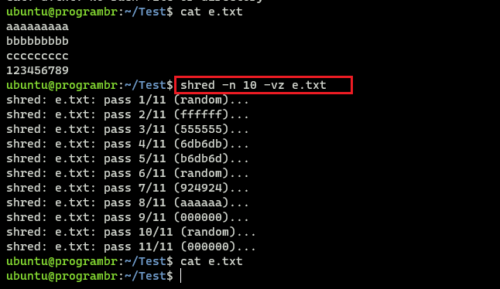
shred -n 10 -vz e.txt
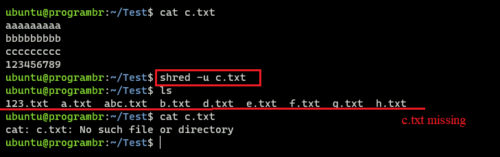
shred -u c.txt
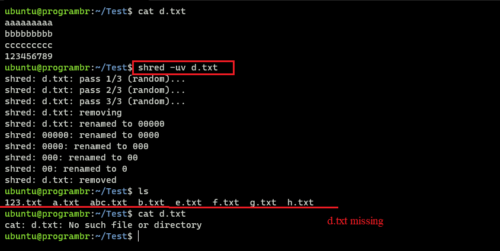
shred -uv d.txt
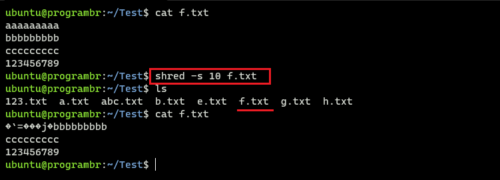
shred -s 10 f.txt
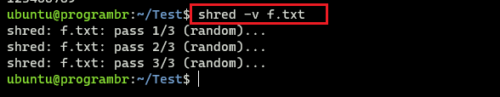
shred -v f.txt
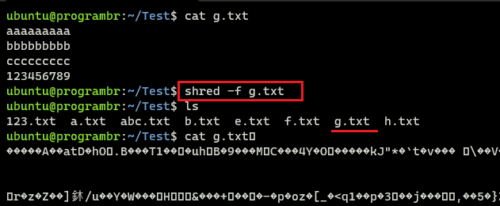
shred -f g.txt
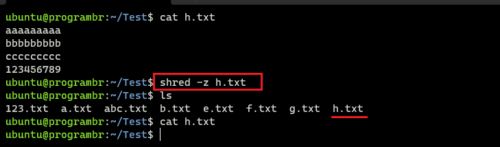
shred -z h.txt
Linux command with examples
A |
| adduser | addgroup | alias | anacron | apt | aptitude | arp | at | atq | atrm | awk |
B |
| basename | banner | batch | bc | bg | bzip |
C |
| cat | cal | cd | chgrp | chown | cksum | chmod | clear | cmp | comm | cp |
D |
| date | dd | df | diff | dir | dmidecode | du |
E |
| echo | eject | env | exit | expr |
F |
| factor | find | free |
G |
| grep | groups | gunzip | gzip |
H |
| head | history | hostname | hostnamectl | htop | hwclock | hwinfo |
I |
| id | ifconfig | ionice | iostat | ip | iptables | iw | iwlist |
J |
K |
| kill | kmod |
L |
| last | less | ln | locate | login | lp | ls | lshw | lscpu | lsof | lsusb |
M |
| man | mdsum | mkdir | more| mv |
N |
| nano | nc | neofetch | netcat | netstat | nice | nmap | nproc |
O |
| openssl |
P |
| passwd | pidof | ping | pr | ps | pwd | pstree |
Q |
R |
| rdiff-backup | reboot | rename | rm | rmdir | rnmod |
S |
| scp | shred | shutdown | sleep | sort | split | ssh | stat | su | sudo | sum |
T |
| tac | tail | talk | tar | tee | time | tree | top | touch | tr |
U |
| unalias | uname | uniq | unzip | uptime | users |
V |
| vim | vi |
W |
| w | wall | watch | wc | wget | whatis | whereis | which | who | whoami |
X |
| xargs |
Y |
| yes | youtube-dl |
Z |
| zcmp | zdiff | zip | zz |