comm command is used in Linux to compare two sorted files line by line and returns the unique lines and common lines of the files in separate columns.
Syntax for comm command
comm [option] file1 file2
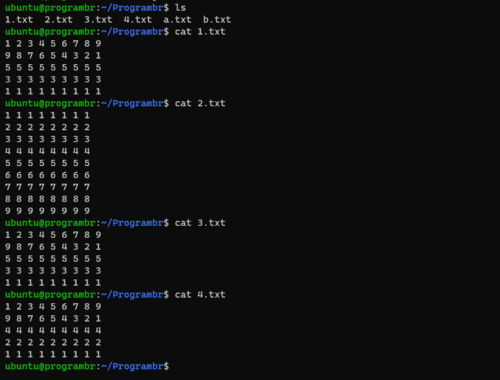
Here is a list and contents of text files, used for comm command in this tutorial.
Uses of comm command with example
Compare two files
comm file1 file2
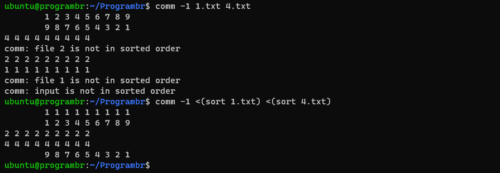
Lines unique to first file
comm -1 file1 file2
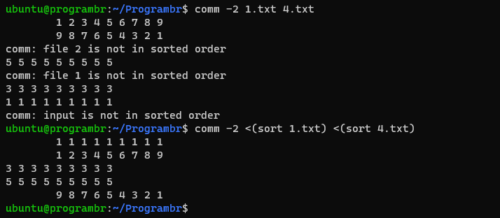
Lines unique to second file
comm -2 file1 file2
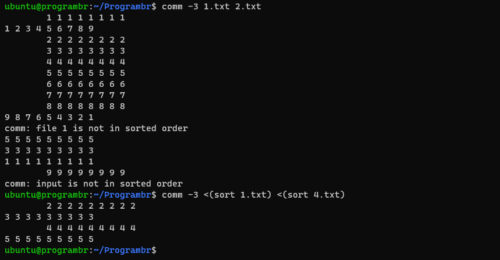
lines common to both files
comm -3 file1 file2
Suppress multiple columns
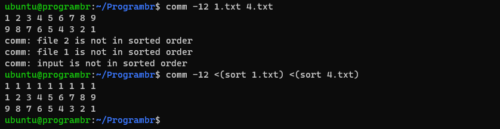
comm -12 file1 file2
cmp command with – -check-order option
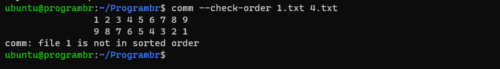
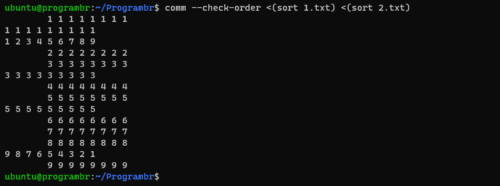
comm --check-order file1 file2
cmp command with – -check-order option
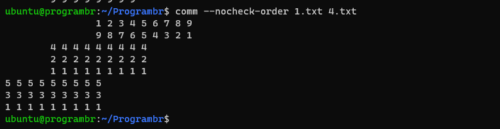
comm --nocheck-order file1 file2
cmp command with –output-delimiter=STR option
comm --output-delimiter=STR file1 file2
cmp command with –total option
comm --total file1 file2
A |
| adduser | addgroup | alias | anacron | apt | aptitude | arp | at | atq | atrm | awk |
B |
| basename | banner | batch | bc | bg | bzip |
C |
| cat | cal | cd | chgrp | chown | cksum | chmod | clear | cmp | comm | cp |
D |
| date | dd | df | diff | dir | dmidecode | du |
E |
| echo | eject | env | exit | expr |
F |
| factor | find | free |
G |
| grep | groups | gunzip | gzip |
H |
| head | history | hostname | hostnamectl | htop | hwclock | hwinfo |
I |
| id | ifconfig | ionice | iostat | ip | iptables | iw | iwlist |
J |
K |
| kill | kmod |
L |
| last | less | ln | locate | login | lp | ls | lshw | lscpu | lsof | lsusb |
M |
| man | mdsum | mkdir | more| mv |
N |
| nano | nc | neofetch | netcat | netstat | nice | nmap | nproc |
O |
| openssl |
P |
| passwd | pidof | ping | pr | ps | pwd | pstree |
Q |
R |
| rdiff-backup | reboot | rename | rm | rmdir | rnmod |
S |
| scp | shred | shutdown | sleep | sort | split | ssh | stat | su | sudo | sum |
T |
| tac | tail | talk | tar | tee | time | tree | top | touch | tr |
U |
| unalias | uname | uniq | unzip | uptime | users |
V |
| vim | vi |
W |
| w | wall | watch | wc | wget | whatis | whereis | which | who | whoami |
X |
| xargs |
Y |
| yes | youtube-dl |
Z |
| zcmp | zdiff | zip | zz |