The main purpose of the w command is to monitor users. w command in Linux displays currently logged-in users and what they are doing. It also shows the system load average, login time, idle time, from where users are logged in etc. In this tutorial you will learn about w command in Linux/Unix and use of w command with example
Understand the output of w command
when we use w command in Linux/Unix machine, the output header mainly displays USER, TTY, FROM, LOGIN@, IDLE, JCPU, PCPU, and WHAT. Now, let’s understand the meaning of these output headers.
- USER: currently logged in user’s name
- TTY: Name of terminal
- FROM: remote hostname or name of the terminal or IP address.
- LOGIN@: Login time (24 hour format)
- IDLE: Time since the user last used the terminal
- JCPU: Total run time.
- PCPU: Elapsed time
- WHAT: what currently logged in users are doing
Syntax of w command
w [options][username]
Uses of w command with examples
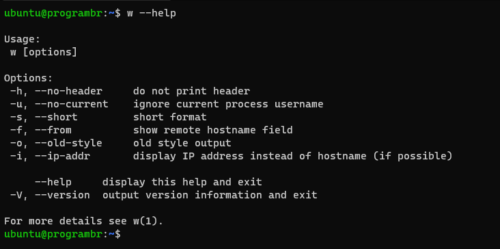
To get help about w command and know the options available with w command, use w –help command.
w --help
Version of w Command
To display the installed version of w command use w -V or w –version command.
w -V
Using w command
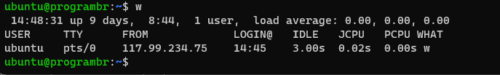
w command without any options displays the system time, up time, Number of users, average system load in last 1 minute, 5 minutes, 15 minutes, and username, tty, from, login@, idle, jcpu, pcpu, what of currently logged-in users.
w
Display output of w command without any header
To display the output of w command without any header (system time, up time, Number of users, average system load in last 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, and username, tty, from, login@, idle, jcpu, pcpu, and what) use w command with -h option
w -h
w -h
Ingnore username while displaying the current process and CPU times
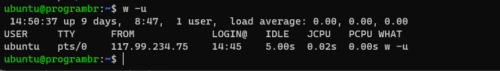
To display CPU times and current processes ignoring the username, use w command with -u option w -u.
w -u
Display in short format
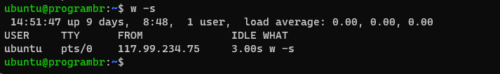
w command with -s option display output in short format. w command with -s option will not print the login@, JCPU and PCPU times.
w -s
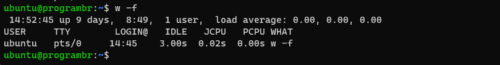
Show/Hide the FROM field
Use w command with -f option to toggle the FROM field. w command with -f option show/hide FROM field depends on the default option in Linux distribution. i.e FROM field is shown in ubuntu and hidden in Arch Linux by default.
w -f
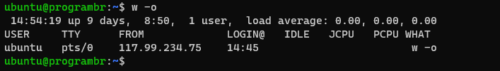
Display old style output
w command with -o option hides IDLE, JCPU, and PCPU times shorter than 1 minute.
w -o
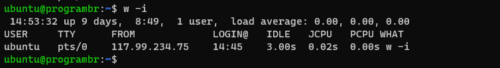
Display IP address in w command’s output FROM field
By default w command display the remote hostname or name of the terminal in FROM field. Use w command with -i option to display IP address in FROM field.
w -i
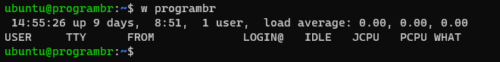
Display specific user information
To display specific user information or monitor any specific user, use
w usernamecommand. Change the username with your computer’s username.
w username
Here I am using programbr as a username.
w programbr
[insert page=’linux-commands-with-example’ display=’content’]