wc command is an abbreviation for word count and wc command is mainly used for counting purpose. It is used to count the number of characters, words, new lines, and bytes in a file or standard input. In this tutorial, you will learn about wc command in Linux/Unix and the uses of wc command with examples.
Syntax for wc command
wc [option] [file]
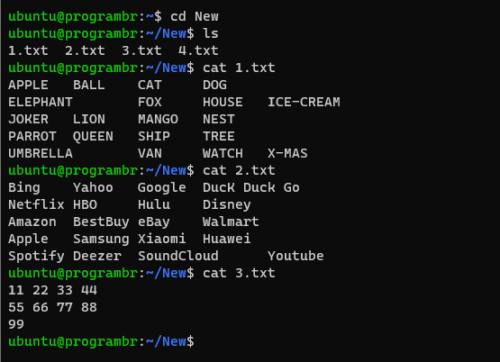
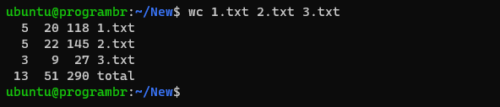
Here is the list of files and file content, which I am going to use in this tutorial. Contents of 1.txt and 2.txt are in words and contents of 3.txt are in integer.
Uses of wc command with examples
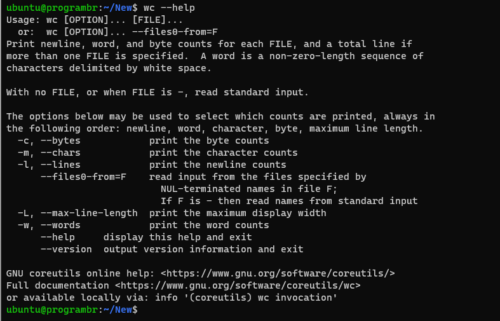
To get help about wc command and find available options for wc command, use wc --help command.
wc --help
Display current version
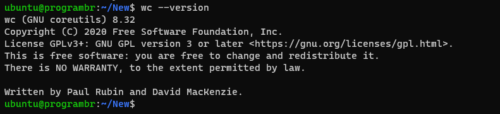
To display current installed version of wc command, use wc --version command.
wc --version
Using wc command with single file
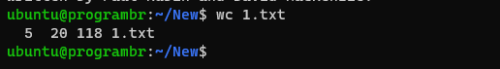
By default, wc command displays the number of new lines, words, and bytes in a file and filename respectively. To use wc command follow the syntax wc filename. Replace the filename with your existing filename or the existing filename with location.
wc filename
Using wc command with multiple files
To use wc command with multiple files and display the number of new lines, words, and bytes in a file and filename of multiple file, follow the syntax wc file1 file2 ....
wc file1 file2 ...
Display number of Bytes only
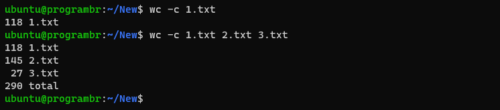
Use wc command with -c option to display only number of Bytes or Byte count in any file. Follow the following syntax to display only number of Bytes or Byte count in any file.
For single file
wc -c filename
For multiple files
wc -c file1 file2 ...
Display number of characters only
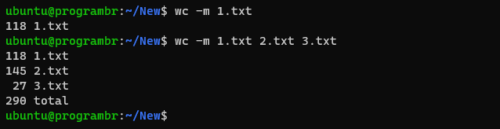
Use wc command with -m option to display only the number of characters or characters count in any file. Follow the following syntax to display only the number of characters or characters count in any file.
For single file
wc -m filename
For multiple files
wc -m file1 file2 ...
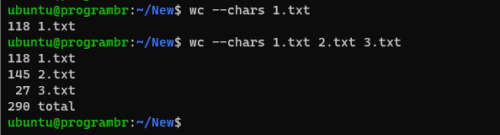
Alternatively, You can also follow the following syntax to display only the number of characters or characters count in any file.
For single file
wc --chars filename
For multiple files
wc --chars file1 file2
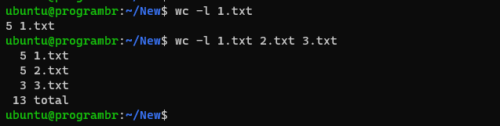
Display number of new lines only
Use wc command with -l option to display only the number of new lines or new lines count in any file. Follow the following syntax to display only the number of new lines or new lines count in any file.
For single file
wc -l filename
For multiple file
wc -l file1 file2 ...
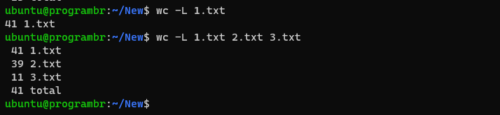
Display length of longest line only
Use wc command with -L option to display only the length of longest line in any file. Follow the following syntax to display only the length of longest line in any file.
For single file
wc -L filename
For multiple files
wc -L file1 file2 ...
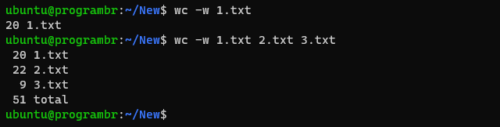
Display number of words only
Use wc command with -w option to display only number of words or words count in any file. Follow the following syntax to display only number of words or words count in any file.
For single file
wc -w filename
For multiple files
wc -w file1 file2 ...
Alternatively, You can also follow the following syntax to display only the number of words or words count in any file.
For single file
wc --words file
For multiple files
wc --words file1 file2 ...
[insert page=’linux-commands-with-example’ display=’content’]